Transient transfection analysis
1. Instant Transfection Analysis
At present, there are many functional analysis methods for studying transcription regulation. The most commonly used method is transient transfection analysis. This method is to introduce a plasmid containing the regulatory region of interest to cultured cells through a certain transfection procedure. In typical cases, The regulatory region regulates the transcription of the "reporter gene". The reporter gene is a gene that is easily detected correctly at both the mRNA and protein levels. After the resulting plasmid is transcribed in cultured cells, the mRNA synthesized from the reporter gene is measured at a specific time Or protein, to evaluate the activity of the regulatory region. This analysis method is called transient transfection analysis, because the plasmid is still present in an additional form at this time, rarely integrated into the host genome. Therefore, the mRNA or protein product must be in the short Measurement within a period of time (1 to 3 days), otherwise the plasmid will be degraded or diluted as the cell grows and divides. Although the transient transfection analysis method has many limitations, this method is still commonly used for cis-acting DNA Preliminary analysis of sequences and trans factors that regulate gene expression.
The transient transfection analysis method is fast, simple, and easy to quantify the results, so it has become the preferred method for promoter function analysis.
The transient transfection analysis method also has two main limitations: first, in the transfected cells, the artificial conformation and copy number of the plasmid may cause specific regulatory elements to be inactivated or have specific functions; second, the transient transfection analysis method cannot It is used to detect those studies that need to be induced or differentiated for more than 48-72 hours.
2. Stable transfection analysis
For regulatory regions that do not exhibit the expected activity in transient transfection analysis, or regulatory regions that rely on specific chromatin structure, stable transfection analysis can be used, that is, the target gene regulatory plasmid containing the reporter gene is stably integrated into the genome. In addition, drug resistance genes (such as dominant selection marker genes) controlled by constitutive promoters need to be stably integrated into the genome for analysis. Drug resistance genes can be on the same plasmid as the reporter gene or on different plasmids. Transfect the cultured cells with the plasmid containing the reporter gene and the drug resistance gene, add a drug that can kill the cells that express the drug resistance gene instability, and part of the plasmid is stably integrated into the chromosome. In most cases, there are many in the cell The two plasmid molecules are connected to each other to form a concatemer, and the concatemer is randomly integrated into the genome of the concatemer, so each cell that is stably transfected has a unique integration site. Then the reporter gene in the cell that is stably transfected is determined by Activity to determine the activity of the regulatory region of interest.
The main advantage of the stable transfection analysis method is that the regulatory regions and reporter genes that are analyzed are usually located in an almost natural chromatin conformation, with an almost natural copy number, these characteristics allow the regulatory region to more accurately simulate normal function. In the transfection analysis, due to the selective amplification of the transfected cells, it overcomes the shortcomings of sub-transient cells that absorb less DNA. Another feature of stable transfection analysis is that there is no time limit for subsequent transcription analysis. Therefore, Stable transfection is very useful for studies that require a relatively long time. The disadvantage of stable transfection analysis is that drug screening and cell expansion are required, so the operation is difficult and requires a long time.
3. In vitro transcription analysis
The in vitro transcription analysis method is suitable for cells that are difficult to transfect, cannot produce a promoter with detectable activity in the transfection analysis, or conduct more advanced studies of gene regulation. A significant feature of this analysis method is that it does not require the determination of effective transfection conditions In addition, antibodies can be added to the in vitro reaction system to add or remove certain transcription factors to evaluate the function of specific transcription factors.
4. Transgenic analysis
The transgenic analysis method is to stably integrate the reporter gene and the regulatory region of interest into the animal genome to detect the precise activity of the regulatory region in the natural sequence. This analysis method can be used to confirm the specific regulatory region or Regulatory elements.
5. Homologous recombination analysis
Homologous recombination analysis is rarely used, only the endogenous genes are manipulated in the cultured cell or animal genome.
In general, we according to your size(cardboard box packaging) and structure to make the fine corrugated packing carton through three or five layers corrugated board. The outer liner can choose Kraft paper, art paper, paperboard, coated paper. On the surface of corrugated carton or corrugated Paper Box can print beautiful and colorful graphics and images. In this way, not only the corrugated box played a protective effect, and propaganda and beautify the inner goods. This make more and more corrugated carton as terminal sales packaging.
Our production process of corrugated box as a follow:
1. Carefully prepare raw material;
2. Make completed corrugated cardboard;
3. Printing pattern as your design;
4. Die-cut corrugated cardboard;
5. Joint to the flat corrugated carton;
6. QC and put in storage;
7. Delivery according to the agreed date.
The most common structures corrugated box are available.
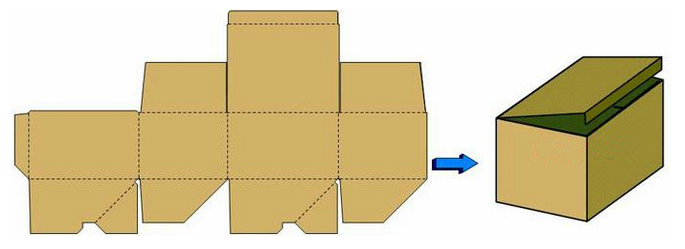
1. Regular slot carton - RSC, also called A - type 1 box, ordinary corrugated box, the flat corrugated box. Please find the picture.
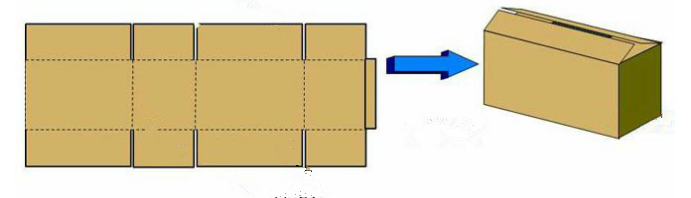
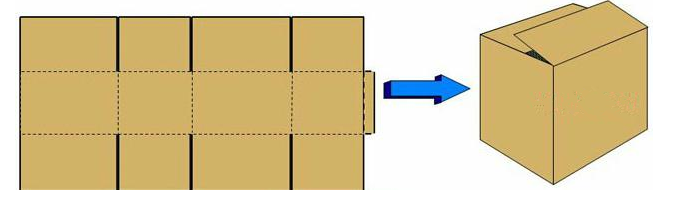
2. Overlapping box – OSC, General design, overlapping part for 2-3 cm.
Design is to prevent tainted, theft or damage when unpacking, common in clothing, small appliances, plastic products, paper products, etc. Please find picture.
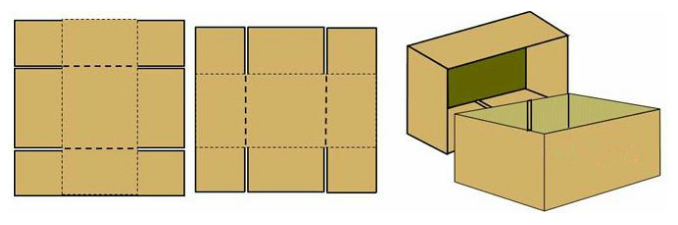
3. Top and bottom corrugated carton is another kind of design of combined corrugated box. The overall compressive capacity of strengthened the protection of the edge.
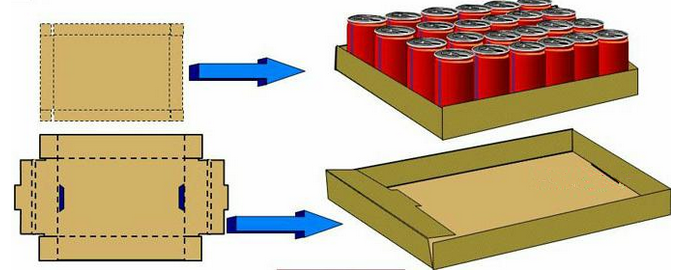
4. Corrugated Tray, Single corrugated board, wire slot or the die cutting processing. Used in the packaging of tinned or boxed products.
5. The lock at the end of the corrugated carton, mainly used in toys, magnetic tape, etc.
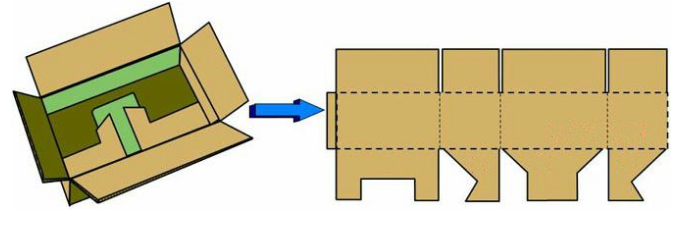
6. Lock bottom plug type folding carton, commonly used in clothing, toys, high value items, glassware, etc. Can be used for single or combination of packaging (box).
Kraft Corrugated Box,Folding Corrugated Box,Plastic Corrugated Box
Shenzhen Haotuanyuan International Trading Co.,Ltd , https://www.luxurypaperbox.com